Introduction to Recommendations#
Recommendations analyze your architecture and business requirements through a sophisticated multi-agent AI system to generate targeted recommendations.
How It Works#
Catio analyzes two primary inputs to generate recommendations:
- Stacks Module Data: Information about your current architecture and historical tech investments
- Context Module Data: Details about your business goals and constraints
Using these inputs, Catio employs a multi-agent AI system that represents both Architects and Employees as AI agents working together to generate highly personalized recommendations.
Types of Recommendations#
Recommendations vary in scope and complexity:
- Single atomic actions (e.g., swap database X for database Y)
- Sequential related actions
- Coarse-grained architectural changes (e.g., implementing a data warehouse)
- Composite actions that decompose into smaller recommendations
Structure of a Recommendation#
Each recommendation contains three components:
Target Architecture
Defines the optimal architecture state:
- Proposed target state for your system
- Technical rationale for the recommendation
- Expected benefits from implementation
Gap Analysis
Evaluates the delta between current and target states:
- Current architecture assessment
- Identified issues or limitations in existing implementation
- Specific differences between current and target architectures
- Technical and business impact of addressing gaps
Recommended Action
Specifies implementation approach:
- Required actions (add, swap, replace, or reuse components)
- Priority classification (adopt now, adopt later, or hold)
- Technical justification for recommended actions
- Expected outcomes and impact metrics
Example Recommendation#
Section: Data Architecture
Recommendation: Choice of database type
Target Architecture: Column-oriented DBMS. Moving to such a data store has significant cost and performance advantages for companies using append-only OLAP data.
Gap Analysis: While you use MongoDB, which is an excellent NoSQL database, it is generally not efficient for append-only OLAP use cases due to the high cost in lookup times as well as the more limited compression levels available for data sets stored as NoSQL.
Recommended Action: Moving from MongoDB to a Column-oriented DBMS could yield significant cost and performance improvements, from 2-10x generally. Considering your company’s highly intensive append-only data volume and reliance on accurate analytics for product features, this improvement could be captured across a very material portion of your total cost and performance envelope.
Architecture Domains#
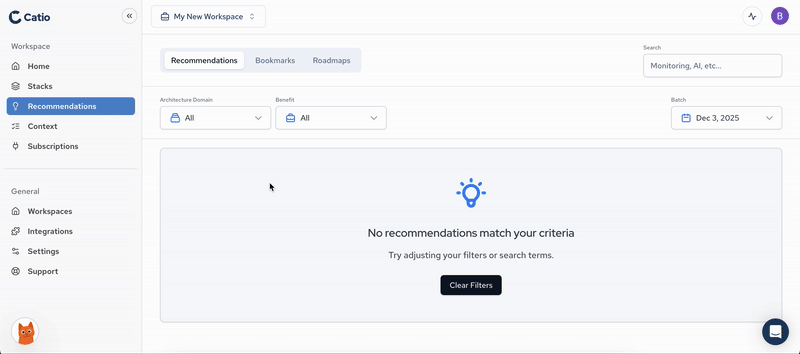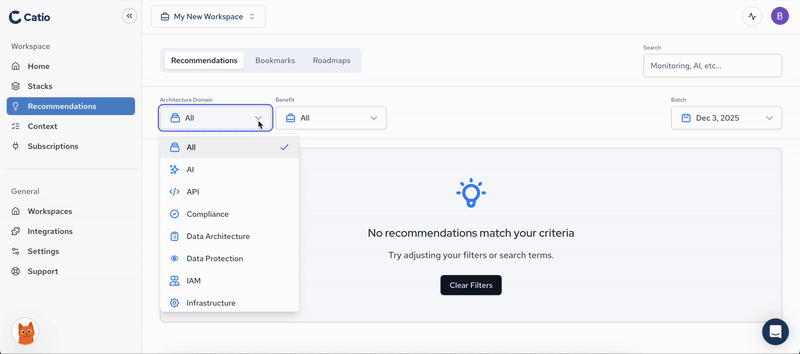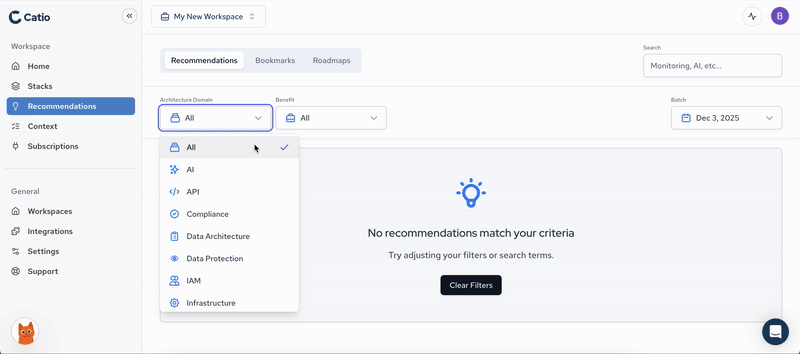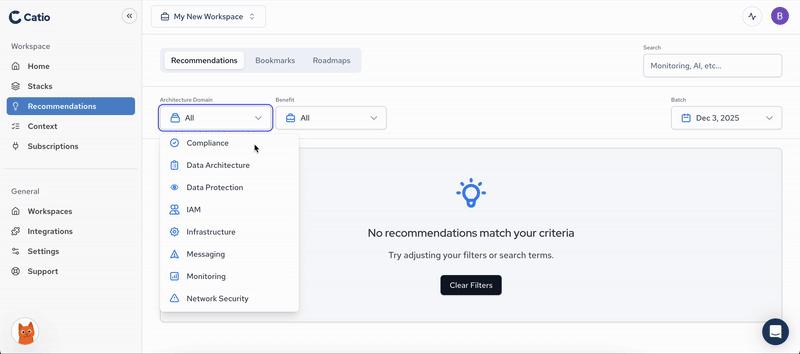
- AI: Artificial Intelligence architecture domain encompassing machine learning models, AI services, and intelligent automation systems
- API: Application Programming Interface architecture domain covering API design, management, gateway services, and integration patterns
- Compliance: Regulatory and policy compliance architecture domain addressing legal requirements, industry standards, and governance frameworks
- Data Architecture: Data storage, processing, and analytics architecture domain including databases, data warehouses, and data pipelines
- Data Protection: Data security and privacy architecture domain covering encryption, access controls, and data governance
- IAM: Identity and Access Management architecture domain managing authentication, authorization, and user permissions
- Infrastructure: Core infrastructure architecture domain including compute resources, networking, and foundational cloud or on-premise systems
- Messaging: Message-based communication architecture domain covering message queues, event streaming, and asynchronous messaging patterns
- Monitoring: Observability and monitoring architecture domain including logging, metrics, tracing, and alerting systems
- Network Security: Network protection architecture domain covering firewalls, intrusion detection, DDoS protection, and secure network design